
Kenji Watanabe, Kuniyoshi Iwabuchi, Jinghua Sun, Yuri Tsuji, Tokio Tani, Kazuaki Tokunaga, Takayasu Date, Mitsumasa Hashimoto, Masaru Yamaizumi, and Satoshi Tateishi (2009) RAD18 promotes DNA double-strand break repair during G1 phase through chromatin retention of 53BP1. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, (7) 2176-2193
Recruitment of RAD18 to stalled replication forks facilitates monoubiquitination of PCNA during S-phase, promoting translesion synthesis at sites of UV irradiation-induced DNA damage. In this study, we show that RAD18 is also recruited to ionizing radiation (IR)-induced sites of DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) forming foci which are co-localized with 53BP1, NBS1, phosphorylated ATM, BRCA1, and γ-H2AX. RAD18 associates with 53BP1 and is recruited to DSB sites in a 53BP1-dependent manner specifically during G1-phase , RAD18 monoubiquitinates KBD domain of 53BP1 at lysine 1268 in vitro . A mono-ubiquitination-resistant 53BP1 mutant harboring a substitution at lysine 1268 is not retained efficiently at the chromatin in the vicinity of DSBs. In Rad18 -null cells, retention of 53BP1 foci , efficiency of DSB repair, and post-irradiation viability are impaired compared with wild-type cells. Taken together, these results suggest that RAD18 promotes 53BP1-directed DSB repair by enhancing retention of 53BP1, possibly through an interaction between RAD18 and 53BP1 and the modification of 53BP1.
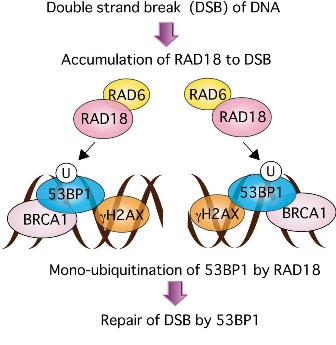
Figure: Model for 53BP1-directed DSB repair promoted by RAD18.
DNA is broken in cells with ionizing irradiation or treatment with genotoxin reagents. RAD18 is recruited to ionizing radiation (IR)-induced sites of DSBs forming foci which are co-localized with 53BP1, NBS1, phosphorylated ATM, BRCA1, and γ-H2AX. On the sites, RAD18 mono-ubiquitinates 53BP1 at lysine 1268. RAD18 promotes 53BP1-directed DSB repair by enhancing retention of 53BP1 on chromatin.