
Masaji Sakaguchi, Sazia Sharmin, Atsuhiro Taguchi, Tomoko Ohmori, Sayoko Fujimura, Takaya Abe, Hiroshi Kiyonari, Yoshihiro Komatsu, Yuji Mishina, Makoto Asashima, Eiichi Araki, and Ryuichi Nishinakamura (2013) The phosphatase Dullard negatively regulates BMP signalling and is essential for nephron maintenance after birth. Nature Communications 4: 1398. (doi: 10.1038/ncomms2408)
Most kidney nephron components, including glomeruli and renal tubules, derive from the metanephric mesenchyme. The overall differentiation into each component finishes at birth, but the molecular events linking the perinatal and adult kidneys remain elusive. Dullard was cloned from Xenopus kidneys, and encodes a phosphatase that negatively regulates BMP signalling. Here we report that Dullard deletion in the murine metanephric mesenchyme leads to failure of nephron maintenance after birth, resulting in lethality before adulthood. The nephron components are lost by massive apoptosis within 3 weeks after birth, leading to formation of a large hollow with a thin-layered cortex and medulla. Phosphorylated Smad1/5/8 is upregulated in the mutant nephrons, probably through cell-autonomous inhibitory effects of Dullard on BMP signalling. Importantly, administration of the BMP receptor kinase inhibitor LDN-193189 partially rescued the defects caused by Dullard deletion. Thus, Dullard keeps BMP signalling at an appropriate level, which is required for nephron maintenance in the postnatal period.
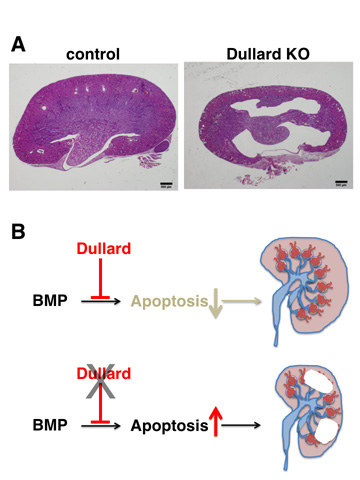
Figure
Dullard negatively regulates BMP signalling and is essential for nephron maintenance after birth.
A. In the absence of Dullard, the nephron components are lost by massive apoptosis within 3 weeks after birth, leading to formation of a large hollow.
B. Dullard keeps BMP signalling at an appropriate level, which is required for nephron maintenance in the postnatal period.