
Yohei Sasagawa, Kunitoshi Yamanaka, Teru Ogura (2007) ER E3 ubiquitin ligase HRD-1 and its specific partner chaperone BiP play important role in ERAD and developmental growth in Caenorhabditis elegans
p97/VCP/Cdc48p belongs to the AAA (ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities) family and has been indicated to be required for mitotic M-phase. We previously reported that simultaneous depletion of two p97 homologues, CDC-48.1 and CDC-48.2, in Caenorhabditis elegans caused the complete embryonic lethality, and that a large number of vacuole-like structures were observed in the dead embryos. However, cellular functions of p97 in embryogenesis have not been revealed. In this study, we analyzed effects of p97 depletion on meiotic progression. Simultaneous depletion of both p97 resulted in the formation of aberrant multinucleate cells and sometimes ectopic furrows in embryos. Importantly, meiotic chromosomes were not divided at meiotic metaphase I in p97-depleted embryos, although spindle formation and disassembly occurred. Furthermore, we found that chromosome condensation was significantly reduced in p97-depleted oocytes. Taken these results altogether, we propose that C. elegans p97 plays an important role in the progression of meiosis.
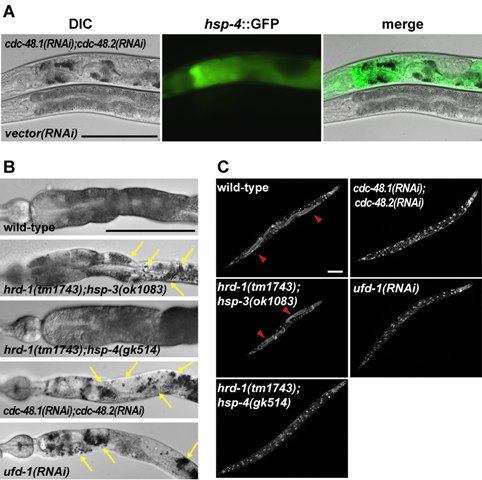
Figure: Evidence for genetic interaction between HRD-1 and BiP.
A L1 larvae were used for feeding RNAi and observed after 48 h incubation. DIC and fluorescent micrographs of vector(RNAi) and cdc-48.1(RNAi);cdc-48.2(RNAi) are shown.
B Photomicrographs obtained 3 days after lay of worms containing indicated mutations. For hrd-1(tm1743);hsp-3(ok1083) mutant, a photomicrograph obtained 6 days after lay is also shown. Intestines of indicated mutant worms were dissected and observed. Yellow arrows show some of typical dark staining large granules.
C Indicated mutant worms were fixed, stained with DAPI and observed. Red arrowheads represent one arm-gonad. Scale bar: 0.1 mm in all images.